Acetic Acid Strong Or Weak
Ethanoic Acetic acid and NaOH Reaction pH change Titration. Acetic acid also known as ethanoic acid is a weak acid with the chemical formula CH 3 COOH.

Difference Between Strong And Weak Acid Difference Between

Why Re Hydrochloric Acid Nitric Acid And Sulfuric Acid Strong Acids While Hydrofluoric Acid And Acetic Acid Weak Acids
HC 2H 3O 2 aq H 2O l H 3O aq C 2H 3O 2 aq Similarly for the weak acid benzoic acid the reaction.
Acetic acid strong or weak. A strong acid is generally a compound that dissociates completely or is 100 ionized in a solution to yield H ions which means no undissociated acid remains in the solution all moles of acid completely break off and release a lot of H ions. The reaction of the weak acid acetic acid with a strong base NaOH can be seen below. CH 3 CO 2 H.
In order for the approach taken to the calculation for acetic acid to work the acid has to be just right. Typically dissociate less than 100 in water. Although acetic acid is very soluble in water almost all of the acetic acid in solution exists in the form of neutral molecules less than 1 dissociates.
At equilibrium both the acid and the conjugate base are present in solution. Examples include acetic acid CH 3 COOH the main component of vinegar and formic acid HCOOH the acid responsible for the sting of ant bites. In the reaction the acid and base react in.
It has a pungent smell and a sour taste. The main difference between strong and weak acids is that strong acids dissociate completely in aqueous solutions whereas weak acids partially dissociate in aqueous. Namely species of the genus Gluconobacter have potent catalytic activity in the oxidation of ethanol d.
Glacial acetic acid is a much weaker base than water so the amide behaves as a strong base in this medium. For example production of gluconic acid from d-glucose and ketogenic activity from glycerol is weak to negligible in Acetobacter species but strong in Gluconobacter. State your solution to the problem is acetic acid a strong or weak electrolyte.
Sulfuric acid is unusual in that it is a strong acid when it donates its first proton Equation ref438 but a weak acid when it donates its second proton Equation ref439 as indicated by the single and double arrows. The reaction of Sodium hydroxide and Acetic acid also called Ethanoic acid represents a net ionic equation involving a strong base and a weak acid. PH See the equations used to make this calculation.
This means that a weak acid does not donate all of its hydrogen ions H in a solution. But it also must be strong enough that the H 3 O ions from the acid overwhelm the dissociation of water. A 10 molar CH 3 COOH solution for example has a pH of 237.
AH H 2 O A-aq H 3 O aq. To Learn about the structure of Acetic acid its preparations chemical physical properties uses and FAQs. Although both substances are acids you wouldnt use muriatic acid in salad dressing and vinegar is ineffective in cleaning bricks or concrete.
Acetic acid HC 2 H 3 O 2 HOAc weak electrolyte molecules and some ions hydrogen chloride HCl strong electrolyte ions only 3. Many hardware stores sell muriatic acid a 6 M solution of hydrochloric acid HClaq to clean bricks and concrete. Although its mechanism of action is not fully known undissociated acetic acid may enhance lipid solubility allowing increased fatty acid accumulation on the cell membrane or in other cell wall structures.
While acids tend to be corrosive the strongest superacids carboranes are actually not corrosive and could be held in your hand. Examples of strong acids and bases are given in the table below. Weak acids have very small values for K a and therefore higher values for pK a compared to strong acids which have very large K a values and slightly negative pK a values.
Strong and Weak Acids and Bases. Because it does not dissociate 100 we can say that the dissociation of a weak acid is an equilibrium process. The reason is that sulfuric acid is highly corrosive while acetic acid is not as active.
And insert Ka value of the weak acid0001 is input as 1E-3 calculate. A sufficiently concentrated weak acid can still produce a low pH readout. Its conjugate base is the acetate ion with K b 10 14 K a 57 x 10 10 from the relationship K a K b 10 14 which certainly does not correspond to a strong base.
The concentration of the solution greatly affects the dissociation to form the hydrogen ion and the conjugate base acetate CH 3 COO At a concentration comparable to that in vinegar 10 M the pH is around 24 and only around 04 percent of the acetic acid molecules are dissociated. Acetic Acid CH3COOH- Acetic Acid is an organic compound with formula CH3COOHVinegar is a water solution of acetic acid containing 5-8 of acetic acid by volume. You can drink diluted acetic acid the acid found in vinegar yet drinking the same concentration of sulfuric acid would give you a chemical burn.
The conjugate of a weak acid is often a weak base and vice versa. To check If Nitric acidHNO 3 a strong or weak first we have to take a clear understanding of the differences between strong and weak acids. There are virtually no molecules of a.
Grocery stores sell vinegar which is a 1 M solution of acetic acid. Acetic Acid is a synthetic carboxylic acid with antibacterial and antifungal properties. The titration of a weak acid with a strong base involves the direct transfer of protons from the weak acid to the hydoxide ion.
Strong bases are considered strong electrolytes and will dissociate completely. A weak acid or a weak base only partially dissociates. Acids are classified into two groups known as strong acids and weak acids.
A weak acid is one that does not dissociate completely in solution. Acetic acid is a weak acid some of the acetic acid in the beaker will dissociate to produce extra acetate ions and hydrogen ions. CH 3 COOH aq CH 3 COO - aq H aq So we expect the equilibrium concentration of acetic acid in solution to be less than 0043 mol L -1 and the equilibrium concentration of acetate ions to be more than 0029 mol L -1.
For example acetic acid is a weak acid which has a 175 x 10 5. Acetic acid ethanoic acid CH 3 COOH is not listed as an exception so acetic acid is a weak electrolyte. Acetic acid is a weak acid because it only partially dissociates into its constituent ions when dissolved in water.
Strong acids and strong bases are strong electrolytes eg HClaq H 2 SO 4 aq HClO 4 aq. Main Difference Strong vs Weak Acids. This makes acetic acid a monoprotic acid with a pKa value of 476 in aqueous solution.
Since we arrived at the same answer using both the small acid dissociation constant and the Guidelines we are confident that our answer is correct. The acid-base indicator is organic weak acid or weak bases of which molecular color differs from the ionic color. This means that we will split them apart in the net ionic equation.
It is known to be the active component of vinegar which is a 4 7 solution of acetic acid in water. An acid is a molecule or other species which can donate a proton or accept an electron pair in reactions. For example acetic acid HC 2H 3O 2 dissociates somewhere around 10.
Aqueous ethanoic acetic acid is a carboxylic acidRection of ethanoic acid and aqueous NaOH is a weak acid - strong base reactionSodium ethanoate salt and water are given as products. In aqueous solution each of these essentially ionizes 100. Again there are exceptions to this general pH range.
Glacial acetic acid is used in analytical chemistry for the estimation of weakly alkaline substances such as organic amides. It then can be titrated using a solution in glacial acetic acid of a very strong acid such as perchloric acid. As we discussed earlier acid-base indicator will go through discoloration if dripped by an acid solution or a bases solution.
In other words the acid must be weak enough that C is small compared with the initial concentration of the acid. Visit BYJUS for more content.

Understanding And Using Acids Conduct Science

What Is Glacial Acetic Acid

What Are Strong And Weak Acids In The Following List Of Acids Separate Strong Acids From Weak Acids Hydrochloride Acid Citric Acid Acetic Acid Nitric Acid Formic Acid Sulphuric Acid Target
Is Ch3cooh A Strong Acid Quora
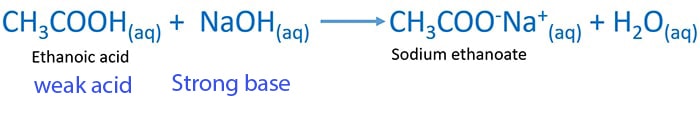
Ethanoic Acetic Acid And Naoh Reaction Ph Change Titration
Where Is The Border Line Between Strong Acids And Weak Acids

Is Ch3cooh An Acid Or Base Strong Vs Weak Acetic Acid
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/list-of-strong-and-weak-acids-603642-v2copy2-5b47abd0c9e77c001a395e55.png)
List Of Common Strong And Weak Acids

0 Response to "Acetic Acid Strong Or Weak"
Post a Comment