Chain Rule Formula
The chain rule for functions of more than one variable involves the partial derivatives with respect to all the independent variables. For instance if f and g are functions then the chain rule expresses the derivative of their composition.

3 Differentiation Rules Copyright Cengage Learning All Rights

Second Order Derivative Of A Chain Rule Regarding Reduction To Canonical Form Mathematics Stack Exchange
The chain rule of differentiation of functions in calculus is presented along with several examples and detailed solutions and comments.
Chain rule formula. The exponential rule is a special case of the chain rule. In Chain Rule for One Independent Variable the left-hand side of the formula for the derivative is not a partial derivative but in Chain Rule for Two Independent Variables it is. To me it seems that there shouldnt be any reason why we cant frame and proof the equation above with the given formula of the chain rule in coordinates.
The chain rule may also be expressed in Leibniz. First I go for the power if any then I go for the rest bit etc. The natural logarithm is usually written lnx or log e x.
Using the chain rule from this section however we can get a nice simple formula for doing this. The derivative of sec x is. The product rule is a formula that is used to determine the derivative of a product of functions.
Warehouse is full and there is a point where 1 extra unit of stock actually involve the massive overhead of getting an extra warehousing location. No the derivative of sec x is NOT same as the derivative of sec-1 x. Here are the results of that.
In calculus the chain rule is a formula that expresses the derivative of the composition of two differentiable functions f and g in terms of the derivatives f and gMore precisely if is the function such that for every x then the chain rule is in Lagranges notation. Well start by differentiating both sides with respect to x. Chain rule for conditional probability.
Show how the tangent approximation formula leads to the chain rule that was used in the previous problem. This calculus video tutorial explains how to find the derivative of trigonometric functions such as sinx cosx tanx secx cscx and cotx. The service level formula given here above is indeed based on a simplistic assumption where costs both storage and stock-outs are stricly linearHowever in practice brutal non-linearities can be found such as.
The approximation formula is. Natural Log ln The Natural Log is the logarithm to the base e where e is an irrational constant approximately equal to 2718281828. Below is one of them.
Recognize the chain rule for a composition of three or. Guillaume de lHôpital a French mathematician also has traces of the. Also in this site Step by Step Calculator to Find Derivatives Using Chain Rule.
However when I actually try to do this my brain completely freezes. Chain Rule of Differentiation in Calculus. The chain rule In order to differentiate a function of a function y fgx that is to find dy dx we need to do two things.
The 10 Rule means that when energy is passed in an ecosystem from one trophic level to the next only ten percent of the energy will be passed on. By power rule and chain rule its derivative is fx 2 sec x ddxsec x 2 sec x sec x tan x 2 sec 2 x tan x. I just solve it by negating each of the bits of the function ie.
Let us remind ourselves of how the chain rule works with two dimensional functionals. A trophic level is the position of an organism. Although the memoir it was first found in contained various mistakes it is apparent that he used chain rule in order to differentiate a polynomial inside of a square root.
Begingroup yeah but I am supposed to use some kind of substitution to apply the chain rule but I dont feel the need to specify substitutes. If we are given the function y fx where x is a function of time. This gives us y fu Next we need to use a formula that is known as the Chain Rule.
In probability theory the chain rule also called the general product rule permits the calculation of any member of the joint distribution of a set of random variables using only conditional probabilitiesThe rule is useful in the study of Bayesian networks which describe a probability distribution in terms of conditional probabilities. This will mean using the chain rule on the left side and the right side will of course differentiate to zero. The chain rule is a method for finding the derivative of composite functions or functions that are made by combining one or more functionsAn example of one of these types of functions is fx 1 x2 which is formed by taking the function 1x and plugging it into the function x2.
If x y z are functions of time then dividing the approximation formula. Related Pages Natural Logarithm Logarithmic Functions Derivative Rules Calculus Lessons. The natural log is the inverse function of the exponential function.
Substitute u gx. Then the derivative of y with respect to t is the derivative of y with respect to x multiplied by the derivative of x with respect to t. The Chain Rule is thought to have first originated from the German mathematician Gottfried W.
Once you have a grasp of the basic idea behind the chain rule the next step is to try your hand at some examples. Is e to the x and the inside function is this polynomial x squared plus 3x1 and so the derivative according to this formula is the same function e to the g of x right so e to the x squared plus 3x1 times g prime of. Let us write the formula for conditional probability in the following format hspace100pt PA cap BPAPBAPBPAB hspace100pt 15 This format is particularly useful in situations when we know the conditional probability but we are interested in the probability of the intersection.
The formula of chain rule for the function y fx where fx is a composite function such that x gt is given as. Apply the chain rule together with the power rule. This is the standard form of chain rule of differentiation formula.
There are a few different ways that the product rule can be represented. Is the Derivative of Sec Inverse x Same as the Derivative of Sec x. ChainRule dy dx dy du du dx wwwmathcentreacuk 2 c mathcentre 2009.
The reason is that in Chain Rule for One Independent Variable z z is ultimately a function of t t alone whereas in Chain Rule for Two Independent Variables z z is a function of both u and v. State the chain rule for the composition of two functions. U and v.
Tree diagrams are useful for deriving formulas for the chain rule for functions of more than one variable where each independent variable also depends on. Given the product of two functions fxgx the derivative of the product of those two functions can be denoted as fxgx. Apply the chain rule and the productquotient rules correctly in combination when both are necessary.
The chain rule is a formula to calculate the derivative of a composition of functions. The Chain Rule is a formula for computing the derivative of the composition of two or more functions. Let us illustrate it with the help of an example.
Or equivalently.

Common Chain Rule Misunderstandings Video Khan Academy

Chain Rule Finding Derivatives Example

Lesson 31

Session 34 The Chain Rule With More Variables Part B Chain Rule Gradient And Directional Derivatives 2 Partial Derivatives Multivariable Calculus Mathematics Mit Opencourseware
Usna Edu

Second Order Derivative Of A Chain Rule Regarding Reduction To Canonical Form Mathematics Stack Exchange

Reverse Chain Rule Edexcel A Level Maths Pure Revision Notes
Mathwords Chain Rule
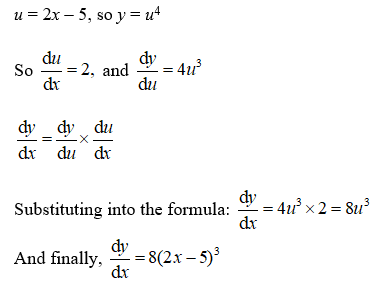


0 Response to "Chain Rule Formula"
Post a Comment