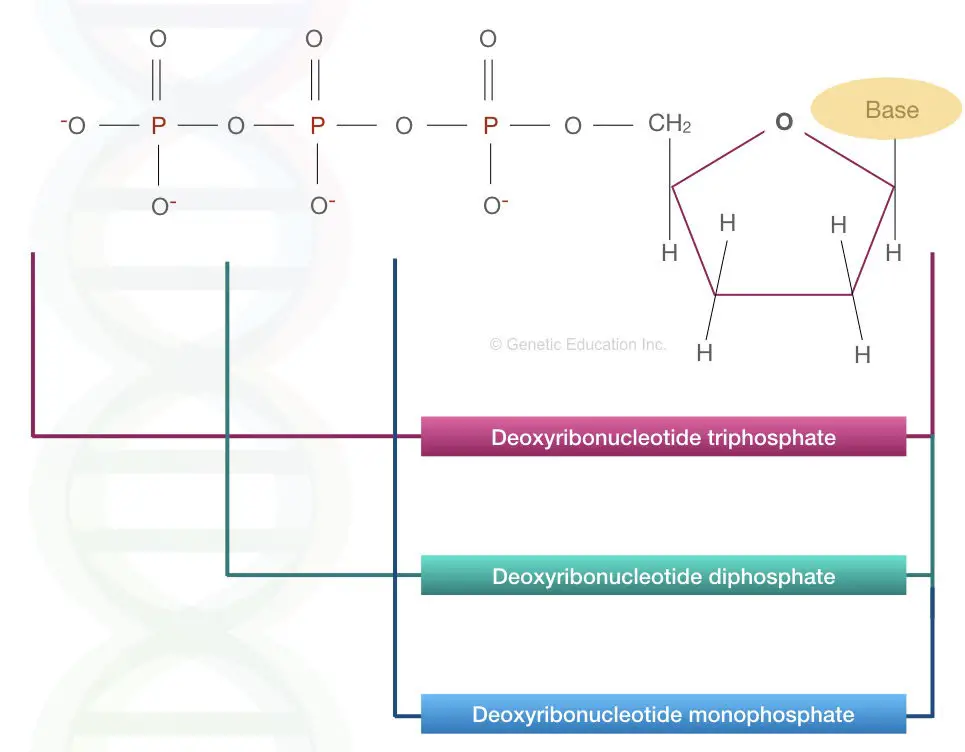
Deoxyribose Nucleoside Triphosphate
This polymerization process leaves a free hydroxyl on the incoming nucleotide on the 3 C of the sugar to serve for the next reaction in chain elongation. It stabilizes m RNA by protecting it from 5 exonuclease.

Deoxyribonucleoside Triphosphate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Nucleoside Vs Nucleotide Difference And Comparison Diffen

Nucleoside Phosphate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
An adenine-containing nucleoside triphosphate that serves as a store of free energy in the cell.

Deoxyribose nucleoside triphosphate. These five carbons are numbered 1 spoken as one-prime 2 etc. Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. 2-deoxyribose which is a pentose a type of sugar composed of five carbon atoms.
The sugar is ribose in the case of RNA deoxyribose in DNA. A nucleoside consists simply of a nucleobase also termed a nitrogenous base and a five-carbon sugar ribose or 2-deoxyribose whereas a nucleotide is composed of a nucleobase a five-carbon sugar and one or more phosphate groups. Each nucleoside triphosphate is made up of three phosphates represented here by yellow spheres a deoxyribose sugar beige rectangle and one of four bases differently colored cylinders.
It is an example of a nucleotideThey are the molecular precursors of both DNA and RNA which are chains of nucleotides made through the processes of DNA replication and transcription. On the other hand when fused with deoxyribose it forms deoxyadenosine. Pentose sugar called 2-deoxyribose.
In a nucleoside the anomeric carbon is linked through a glycosidic bond to the N9 of a purine or the N1 of a. A nucleoside with one or more phosphate groups attached to the sugar is called a nucleotide. Thus nucleoside entry into the cell would no longer be rate-limiting.
Although people tend to refer to the nucleotides by the names of their bases adenine and adenosine arent the same things. นอกจากน นวคลโอไทดยงเปนสารใหพลงงานในกระบวนการเมตาบอลซม Metabolism เชน ATP Adenosine Triphosphate ADP Adenosine Diphosphate และ AMP Adenosine Monophosphate ซงจะแตกตางกนตามจำนวนของ. The image represents the structure of Deoxyribose triphosphate diphosphate and monophosphate.
The nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors are analogues of precursors of the natural purines and pyrimidines involved in DNA transcription initiated by the virus. Read Further on the Structure of DNA. Likewise guanosine thymidine uridine and cytidine are the examples of nucleoside.
If a pentose sugar is attached to a nitrogen base by a glycosidic bond it is called nucleoside. If a sugar either ribose or 2-deoxyribose is added to a nitrogen base the resulting compound is called a nucleoside. Đối với ribose có sự hiện hữu của đường deoxyribose thì tiền tố deoxy có thể được thêm vào trước tên của nucleoside trong mọi.
After uptake nucleosides mostly undergo degradation in the liver. Carbon 1 of the sugar is attached to nitrogen 9 of a purine base or to nitrogen 1 of a pyrimidine base. Eg adenine ribose adenosine.
B A nucleoside triphosphate is added to the 3 end of the DNA releasing a molecule of pyrophosphate. Adenosine is the larger nucleotide molecule made up of adenine ribose or deoxyribose and one or more phosphate groups. This adenosine is an essential component of adenosine triphosphate which is a unit of energy and is utilized during metabolism.
The name of a nucleotide is the corresponding nucleoside name followed by the word monophosphate diphosphate or triphosphate to indicate the number of phosphate groups attached to the sugar. Without an attached phosphate group the sugar attached to one of the bases is known as a nucleoside. Any cell which has a nucleus contains nucleic acid in the form of DNA.
Where it supplies the genes necessary for adenosine triphosphate production the most important source of cellular energy. However such factors as nucleoside metabolism relative contributions to the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pools from endogenous and exogenous sources and possible concomitant effects on cellular metabolism of high nucleoside concentrations should also be considered in studies of this kind Painter and Rasmussen 1964b. An enzyme that seals breaks in DNA strands.
Messenger RNA m-RNA All members of the class function as messengers carrying the information in a gene to the protein synthesizing machinery Structure The 5 terminal end is capped by 7- methyl guanosine triphosphate cap. The cap is involved in the recognition of mRNA by the translating machinery. C A nucleoside diphosphate is added to the 5 end of the DNA releasing a molecule of phosphate.
The structure and function of DNA The phosphate present in nucleotide is triphosphate tri- three when phosphate is not linked with the nucleotide or absent it is called as a nucleoside nucleotide without phosphate is termed as a. The pentose sugar in DNA 2-deoxyribose differs from the sugar in RNA ribose by the absence of a hydroxyl group OH on the 2 carbon of the sugar ring. Adenine is the name of the purine base.
Phosphate of an incoming nucleoside triphosphate NTP to form a phosphoester linkage. The drugs lack the 3-hydroxyl group on the deoxyribose moiety required for normal formation of a phosphodiester bond with the next nucleotide so they terminate further DNA chain elongation. Nucleotides consist of a nucleoside.
Deoxyribose Deprotection Deprotonate Deprotonization DEPT Deshielded Desiccation Desolvation. The names of purine nucleosides end in -osine and the names of pyrimidine nucleosides end in -idine. The nucleoside combines with a phosphate group at.
Deoxycytidine triphosphate dCTP Chú ý. The sugar phosphates are converted to mainstream degradative intermediates via. The 3end of most m-RNAs have a.
A nucleoside comprises the five-carbon sugar and nitrogenous base. A Each deoxyribonucleotide is made up of a sugar called deoxyribose a phosphate group and a nitrogenous basein this case adenine. When fused with ribose adenine forms the nucleoside adenosine.
A nucleoside triphosphate is a molecule containing a nitrogenous base bound to a 5-carbon sugar either ribose or deoxyribose with three phosphate groups bound to the sugar. Cleavage by purine and pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylases gives free bases and ribose- or deoxyribose-1-phosphate. A A nucleoside triphosphate is added to the 5 end of the DNA releasing a molecule of pyrophosphate.
The name 2-deoxyribose indicates that this particular sugar is a derivative of ribose one in which the hydroxyl -OH group attached to the 2-carbon of ribose has been replaced by a hydrogen - H group. 224 The DNA Double Helix. A DNA repair enzyme that cleaves the bond linking a purine or pyrimidine to the deoxyribose of the backbone of a DNA molecule.
Life Sciences Cyberbridge
Deoxynucleotide Triphosphates Dntps And Cyclic Di Amp Analysis Service Creative Proteomics

Expanded Dna Nucleoside Triphosphates Used In This Study Download Scientific Diagram

Nucleoside Triphosphate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Deoxyribonucleoside Triphosphate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
1

Nucleoside Triphosphate Wikipedia
The Function Of Dntps In Pcr Reaction
0 Response to "Deoxyribose Nucleoside Triphosphate"
Post a Comment