Anterior Aspect Of Skull
Forms part of the nasal septum and the nasal cavity. The external cranial base can be subdivided into anterior middle posterior and two lateral parts.


Skull Diagram Anterior View With Labels Part 3 Axial Sk Flickr
Anterior Aspect Of The Skull Advanced Facial And Oral Surgery
The hard palate and the upper jaw.
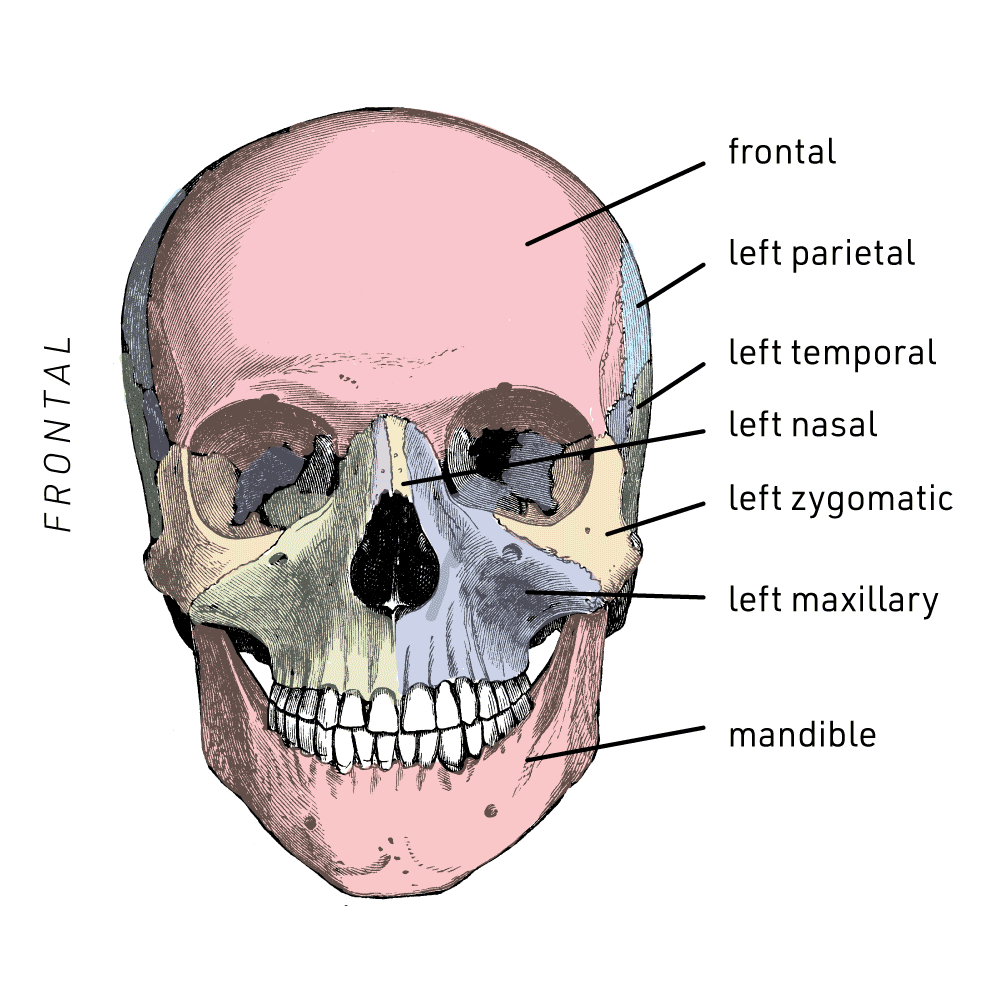
Anterior aspect of skull. Often used to indicate the position of one structure relative to another that is nearer the back of the body. The fontanel allows the fetal skull to be compressed slightly during birth. There are some general features of the skull which are very helpful in determining the sex of the skeletal remains.
The purpose of these pages is to quiz your knowledge on the structures of the skeletal system. NA Forms the posterior aspect and most of the base of the skull. Facies anterior corporis maxillae Anterior surface of the body of maxilla Facies orbitalis corporis maxillae Orbital surface of the body of maxilla Processus frontalis Frontal process of maxilla Processus zygomaticus Zygomatic process Processus alveolaris Alveolar process Margo infraorbitalis Infraorbital margin.
With Matt Salinger Ronny Cox Ned Beatty Darren McGavin. A foramen pl. The pterion is an H shaped region on the lateral aspect of the skull where a number of bones unite with each other.
The disc has anterior A and posterior P bands. External cranial base by Anatomy Next. Review - A comprehensive review of the anterior fontanelle.
Both can result in upper airway oedema and impaired respiration 13During induction of general anaesthesia in patients with cervical instabilities no protective mechanism. Also seen are the upper and lower jaws with their respective teeth Figure 2. It is located in between the mandible and the clavicle connecting the head directly to the torso and contains numerous vital structures.
The largest fontanel is the diamond-shaped anterior fontanel. This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. NA Contributes to the anterior cranial fossa.
Participants of the pterion are the frontal bone the parietal bone the greater wing of the sphenoid bone and the anterior of the squamous part of the temporal bone. The intermediate zone should be between the condyle and the closest portion of the temporal bone in any mouth position. On the inferior aspect of the skull each half of the sphenoid bone forms two thin vertically oriented bony plates.
Left lateral aspect of skull. The neck is the bridge between the head and the rest of the body. In the skull base there are numerous foramina that transmit cranial nerves blood vessels and other structures these are collectively referred to as the cranial foramina.
Dorsalis TA dorsal 2. The cranial capacity in. C113 Malignant neoplasm of anterior wall of nasopharynx C118 Malignant neoplasm of overlapping sites of nasopharynx C12 Malignant neoplasm of pyriform sinus C130 Malignant neoplasm of postcricoid region C131 Malignant neoplasm of aryepiglottic fold hypopharyngeal aspect C132 Malignant neoplasm of posterior wall of hypopharynx.
Anterior aspect of each thigh. Craniosynostosis is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous sutures in a young infants skull prematurely fuses by turning into bone ossification thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull. Fontanelles are a regular feature of infant development in which two segments of bone remain separated leaving an area of fibrous membrane or a soft spot that acts to accommodate growth of the brain without compression by the skull.
A large skull is typically male and a small skull is generally female. The anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes and structures of the face. Sex can also be determined by using the bones of the skull which have an accuracy of 85.
Foramina is an opening that allows the passage of structures from one region to another. The external cranial base is the outer aspect of the skull base. It crosses the knee joint over the patella and also covers the skin over the medial malleolus and the medial aspect of the foot and the great toe.
Basal aspect of skull. Embryology anatomy and clinical considerations. We can divide this part of the skull into five to make it easier to study.
Human anatomy denoting the back surface of the body. The walls of the orbit are formed by contributions from seven bones. The anterior skull has the orbits that house the eyeballs and associated muscles.
Lateral aspect of right mandible. The list of terms. This aspect of the skull contains a lot of important structures including the largest skull foramen.
Out of these the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. Anterolateral thigh and continues down to the medial aspect of the knee and the medial aspect of the posterior lower leg proximal to the medial malleolus L4 dermatome Posterolateral thigh and the anterior tibial area. Atlas 1st cervical vertebra.
Foramen magnum Large opening in the base of the bone which allows the spinal cord to join. The thinner central portion is called the intermediate zone IZ. Medial aspect of right mandible.
Directed by Albert Pyun. Anterior View of Skull. The posterior band is normally located directly on top of the condyle C when the mouth is closed.
Located at the superior margin of the orbit is the supraorbital foramen and below the orbit is the infraorbital foramen. It contains some of the most complex and intricate anatomy in the body and is comprised of numerous organs and tissues with essential structure and function for normal physiology. Because the skull cannot expand perpendicular to the fused suture it compensates by growing more in the direction parallel to the closed sutures.
Axis 2nd cervical vertebra. Contributes to the medial wall of the orbit. The greater wing is best seen on the outside of the lateral skull where it forms a rectangular area immediately anterior to the squamous portion of the temporal bone.
Frozen in the ice for decades Captain America is. The following links will allow you to access real photographs of the human skeletal system. The reported incidence of postoperative respiratory compromise varies from 014 1234This is likely caused by trauma to the anterior soft-tissue and prolonged prone position.
Dorsal aspect of skull. This view of the skull is dominated by the openings of the orbits and the nasal cavity. Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals including humansThe terms typically derived from Latin or Greek roots describe something in its standard anatomical positionThis position provides a definition of what is at the front anterior behind posterior and so on.
Vertebral Column Spine Serving as the axial support of the body the vertebral column or spine extends from the skull which it supports to the pelvis where it transmits the weight of the body to the lower limbs. The frontal zygomatic maxillary palatine ethmoid lacrimal and sphenoid. It extends from the superior incisor teeth to the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone.
In this article we shall look at some of the major cranial foramina and the structures that pass through them.

The Skull Bones Anterior View

Bones Cranium Bones Head Skull Individual Stock Illustration 505305988

File Skull Human Anterior View Svg Wikipedia

Anterior View Of Skull
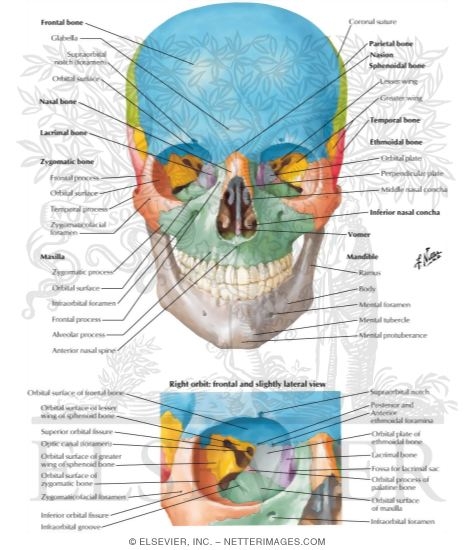
Anterior Aspect Of Skull
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10684/skull-anterior-lateral-views_english.jpg)
Skull Anatomy Structure Bones Quizzes Kenhub

John Hawks Laboratory

Anterior Aspect Of The Skull Diagram Quizlet

0 Response to "Anterior Aspect Of Skull"
Post a Comment