Relative Mass Of Electron
As you may recall e mc 2. 1 TeV 10 12 eV.
Charge

How Much The Mass Of Electron With Relative And Calculate
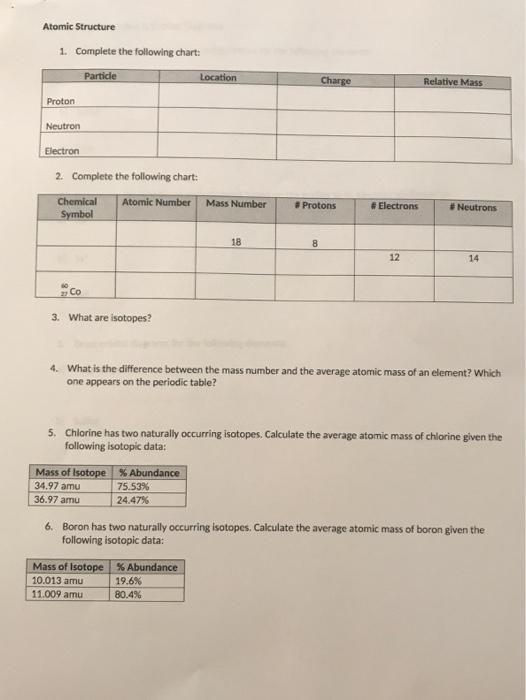
Solved Atomic Structure 1 Complete The Following Chart Chegg Com
Happily to find the mass number all you need to do is round the atomic weight to the nearest whole number.
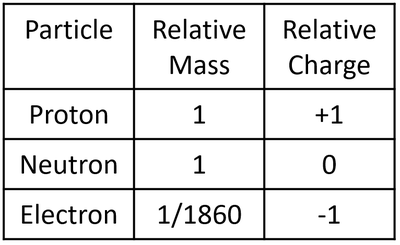
Relative mass of electron. However the nuclear sizes are quite small and need smaller units. The atomic mass is the mass of an atom. The model does not depict electrons as particles moving around the nucleus in a fixed orbit.
The standard atom chosen is carbon-12 isotope. The mass number is a count of the number of particles in an atoms nucleus. The electron cloud is also defined as the region where an electron forms a three-dimensional standing wave the one that does not move relative to the atomic nucleus.
The Nature of Mass Spectra A mass spectrum will usually be presented as a vertical bar graph in which each bar represents an ion having a specific mass-to-charge ratio mz and the length of the bar indicates the relative abundance of the ion. 1 GeV 10 9 eV. The most intense ion is assigned an abundance of 100 and it is referred to as the base peak.
Unfortunately the mass number isnt listed on the Table of Elements. It can be used to find relative isotopic abundance atomic and molecular mass and the structure of a compound. Just like lightbulb filaments however they gradually lose mass to evaporation and eventually break giving them the shortest lifetime of all the sources.
The most commonly used unit is the MeV. I Give the number of protons in an atom of 27 A1. Information about relative isotopic mass and also about the relative abundance of isotopes.
The spectrum is often plotted on a relative abundance scale. The ionized atoms are then separated from neutral particles in a vacuum chamber by an ion guide and detected by a mass spectrometer MS. In our example kryptons mass number is 84 since its atomic weight 8380 rounds up to 84.
The effective mass may be anisotropic and it may even be negative. The result of a Mass Spectrometry is a graph plotting mass per charge against relative abundanceObjects atoms or groups of atoms of different masses may be detected due. Additionally due to their.
Relative mass Relative charge Proton Electron 2 b An atom of element Q contains the same number of neutrons as are found in an atom of 27 A1. Similarly relative isotopic mass referred to as the mass of an atom of an isotope with respect to the. MS 11 Students report calculations to an appropriate number of significant figures given raw data quoted to.
Mass spectrometry can be used to determine relative molecular mass. Atomic and molecular masses are assigned relative to the mass of the carbon isotope 12 C whose atomic weight is defined as exactly 12. The actual mass of 12 C is 12 daltons with one dalton is equal to 1661 10-24 g.
Since the mass of an atom would be extremely small when measured in grams it would be more convenient to measure the masses of atoms relative to a standard atom. The relative isotopic mass is a unitless quantity with respect to some standard mass quantity. The electron relative atomic mass can be measured directly in a Penning trap.
Nuclear energies are very high compared to atomic processes and need larger units. In this module students reconnect with and deepen their understanding of statistics and probability concepts first introduced in Grades 6 7 and 8. Mass spectrometry is a gas phase technique- the sample must be vaporized Electron-impact ionization Sample Inlet 10-7 - 10-8 torr R-H electron beam 70 eV 6700 KJmol.
An atom of Q also contains 14 protons. However the mass of an electron is so small it is considered negligible and not included in the calculation. Electron beams are essential to electron microscopes.
From the free electron mass m0. The atomic mass or relative isotopic mass refers to the mass of a single particle and therefore is tied to a certain specific isotope of an element. Mass Spectrometry is a process by which the atomic mass of atoms or molecules is determined.
A mass spectrum is the plot of relative abundance of ions against their masscharge ratio. Electron i- emitters are found throughout the periodic table from the lightest elements 3 H to the heaviest 255 EsThe product of i--emission can be predicted by assuming that both mass number and charge are. Electron e electron mass m e 9109382616 710 31 kg 17 10 in u m e A re u electron relative atomic mass times u 5485799094524 10 4 u 44 10 10 energy equivalent m ec2 8187104714 10 14 J 17 10 7 in MeV 051099891844 MeV 86 10 8 electron-muon mass ratio m emµ 48363316713 10 3 26 10 8 electron-tau mass ratio m emτ 2.
When an electron passes through a potential difference accelerating voltage field V its kinetic energy with be equal to the energy of the field ie. M u is defined as being 1 12 of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Mass spectrometry can be used to identify elements.
An example EI MS spectrum is presented in Figure 1. The mass-to-charge ratio of the ions is used to separate the elements and the concentration of each element is determined based on the ion signal proportion relative to an internal calibration standard. EV energy in electron volts V the accelerating voltage.
Relative atomic mass symbol. This second definition is actually the relative. An atom of carbon-12 is taken to have a mass of 12 atomic mass unit amu.
1 electron volt 1eV 16 x 10-19 joules 1 MeV 10 6 eV. The atomic mass is carried by the atomic nucleus which occupies only about 10 -12 of the total volume of the atom or less but it contains all the positive charge and at least 9995 of the total mass of. The important point is that the electron in a periodic potential is accelerated relative to the lattice in an applied electric or magnetic.
There are crystals in which the effective mass of the carriers is much larger or much smaller than m0. The mass spectrometer acquires a mass spectrum and displays this data as a histogram of the abundance of the ions that reach the detector according to their mass to charge ratio mz. M mass of the particle 91 X 10-28 v velocity of the particle.
Atomic mass is the sum of all the protons neutrons and electrons in a single atom or molecule. Have high melting points relative to NiCr alloys and have lower work functions. The basic aspect of organic mass spectrometry consist of bombarding the vapour of an organic compound with a beam of energetic electron accelarated from a filament to an energy of 70 eV to form positively charged ions molecular ions.
Molecular weight of the sample formula The mass spectrometer gives the mass to charge ratio mz therefore the sample analyte must be an ion. Electron em- emission is literally the process in which an electron is ejected or emitted from the nucleusWhen this happens the charge on the nucleus increases by one. Though technically incorrect the term is also often used to refer to the average atomic mass of all of the isotopes of one element.
Since both quantities in the ratio are masses the resulting value is dimensionless. It can also be inferred from the spectra of antiprotonic helium atoms helium atoms where one of the electrons has been replaced by an antiproton or from measurements of the electron g. Algebra I Module 2.
Electron configuration Ne 3s 2 3p 1. A r or atomic weight is a dimensionless physical quantity defined as the ratio of the average mass of atoms of a chemical element in a given sample to the atomic mass constantThe atomic mass constant symbol. The relative atomic mass can be taken as the weighted mean mass of an atom of an element compared to the mass of 112 of the mass of an atom in C-12.
Atomic sizes are on the order of 01 nm 1 Angstrom 10-10 m. The mass of a molecule or an ion can be presented in daltons Da or kilodaltons kDa.

Subatomic Particles Particle Symbols Relative Electric Charge Mass

Relative Atomic Charge Key Stage Wiki

Electron Wikipedia
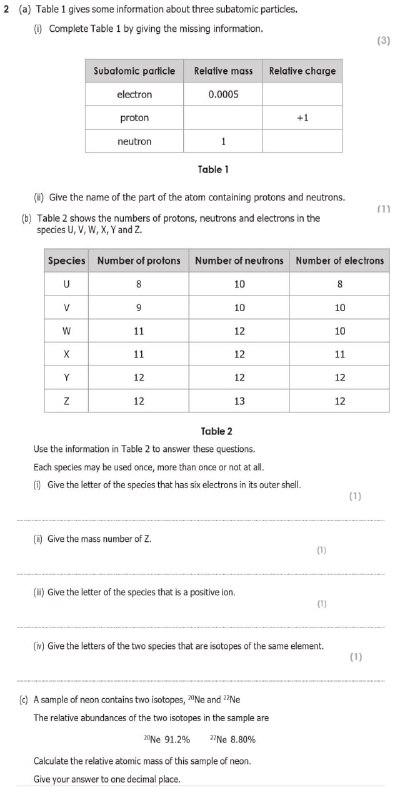
Solved 2 A Table 1 Gives Some Information About Three Chegg Com
Select A Section Introduction Atoms Molecules And Ions Laws And Theories A Brief Historical Introduction 2 1 Laws Of Chemical Combination 2 2 John Dalton And The Atomic Theory Of Matter 2 3 The Divisible Atom 2 4 Atomic Masses 2 5 The Periodic
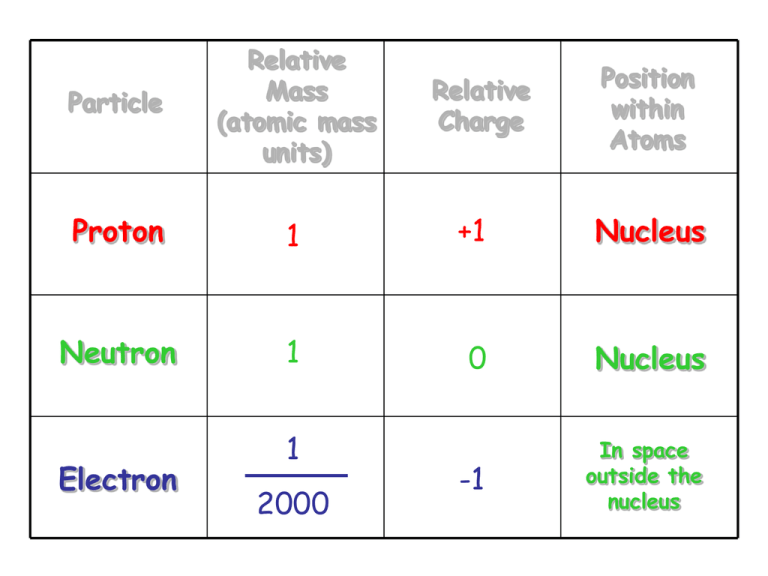
What Element Am I
.bc0e8d3.jpg)
Protons And Neutrons Weigh The Same Electrons Weigh A Little
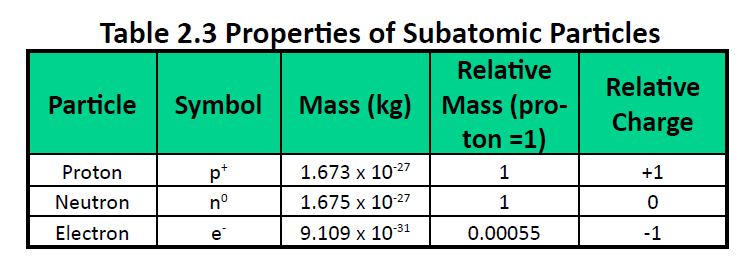
Ch104 Chapter 2 Atoms And The Periodic Table Chemistry

0 Response to "Relative Mass Of Electron"
Post a Comment