Dalton's Law Of Partial Pressure
The total pressure in moist air can therefore be expressed as. Daltons law is related to the ideal gas laws.
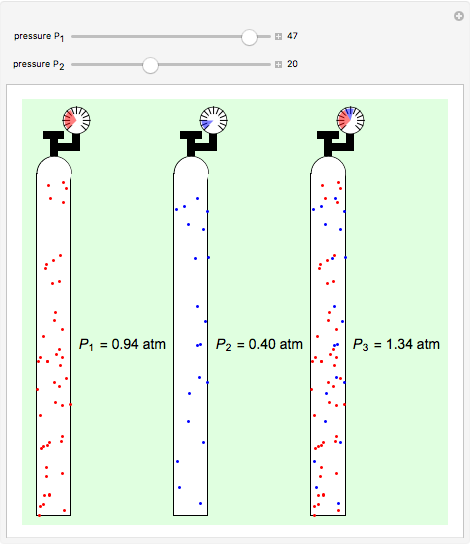
Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressures Wolfram Demonstrations Project
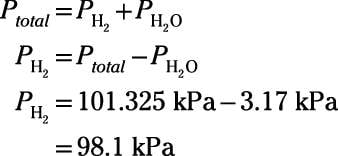
How To Calculate Partial Pressures Using Dalton S Law Dummies
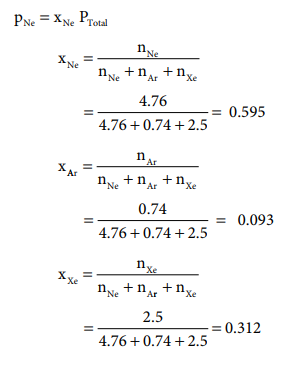
Solved Example Problems Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressures
Understand Daltons Law of Partial Pressures.
Dalton's law of partial pressure. Daltons Law states that. To Learn expressions on Daltons law of partial pressure Examples Videos with FAQs. Thus the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture.
PV nRT where P is pressure V is volume n is the number of moles R is the gas constant and T is temperature. Daltons Law of Partial Pressure. Solved Examples on Daltons Law of Partial Pressure Example 1.
Daltons law can be used to determine the partial pressure of a gas in a mixture. The law used to find partial pressure assumes the temperature of the system is constant and the gas behaves as an ideal gas following the ideal gas law. P i the pressure of component.
This equality arises from the fact that in an ideal gas the molecules are so far apart that they do not interact with each other. Daltons law expresses the fact that the total pressure of a mixture of ideal gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases in the mixture. Partial pressures can also be calculated through the ideal gas law and both methods of Henrys Law.
If the partial pressure of hydrogen is 1 atm find the mole fraction of oxygen in the mixture. P tot P i P 1 P 2 P 3. Daltons law establishes that within a combination of any given gases the total pressure is the same as the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas present in that mixture.
P t total pressure kPa. Identify the law which is stated asFor any solution the partial vapour pressure of each volatile component in the solution isdirectly proportional to its mole fractionaHenrys lawb Raoults lawcDaltons lawdGay-Lussacs Law. P a partial pressure dry air kPa.
To make this problem a little interesting lets assume that youre not familiar with Daltons Law of partial pressures which tells you that the partial pressure of a gas thats part of a gaseous mixture is proportional to that gas mole fraction. A mixture of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas exerts a total pressure of 15 atm on the walls of its container. P Ar 400 - 120.
Also in the 1800s he was the first scientist to explain the behavior of atoms in terms of the measurement of weight. P w partial pressure water vapor kPa. P t p a p w 3.
Daltons Law of Partial Pressure states the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressure of each individual gas. The term partial pressure is used when we have a mixture of two or several gases in the same volume and it expresses the pressure that is caused by each of the induvidual gases in the mixture. If a mixture of ideal gases ie where the molecules dont interact with each other is sealed within a container the gases will diffuse and fill up all of the available space.
Given P hydrogen 1 atm P total 15 atm. The gases present in the container are chemically inert. Daltons law of partial pressures Pressure is the force applied orthogonally over a surface.
Summing their two pressures gives the total pressure. P_i is the partial pressure of gas i chi_i is the mole fraction of gas i in the mixture P_total is the total pressure of the mixture. Vapor pressure and the ideal gas law.
Explanation Based on the kinetic theory of gases a gas will diffuse in a container to fill up the space it is in and does not have any forces of attraction between the molecules. ColorblueulcolorblackP_ i chi_ i P_total Here. P tot the total pressure.
The total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases. This is the currently selected item. Daltons Law P P P.
Written as an equation it looks like this. Thus the partial pressure of a gas P P x is the portion of the total pressure of a gas mixture contributed by a single gas. Heres how you can think about whats going on Lets assume that the mixture is at a pressure P_total a temperature T and occupies a.
Daltons Law immediately follows from this example since each gas is causing 50 of the pressure. If 600 L of nitrogen is collected over water at 400 C when the atmospheric pressure is 7600 mm Hg what is the partial pressure of the nitrogen. Each gas in a mixture creates pressure as if the other gases were not present.
The pressure of any gas within the container is called its partial pressure. Developed by chemist and physicist John Dalton who first advanced the concept of chemical elements being made up of atoms 9 X Research source Daltons Law states that the total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the pressures of each of the gases in the mixture. Since inspired air is 21 oxygen and atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg at sea level the partial pressure of.
Thus the partial pressure of oxygen PO 2 depends mainly on the atmospheres barometric pressure BP and its fractional concentration. Daltons law describes the behavior of nonreactive gases in a gaseous mixture and states that a specific gas type in a mixture exerts its own pressure. In 1803 he revealed the concept of Daltons Law of Partial Pressures.
Calculate the partial pressure of helium and argon if the total pressure inside the container is 400 atm. Daltons law of partial pressures which stated that in a mixture of non-reacting gases the total pressure exerted is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases. Calculations using the ideal gas equation.
Where p 1 p 2 p n represent the partial pressures of each. P He 0300 x 400 atm 120 atm. This empirical law was observed by John Dalton in 1801 and published in 1802.
Visit BYJUS for more content. 7600 mmHg minus 553. Daltons Law or the Law of Partial Pressures states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture.
The total pressure of the gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressure of the component gases. Partial Pressure- Partial Pressure is defined as a container filled with more than one gas each gas exerts pressure. For starters you know that the partial pressure of a gas thats part of a gaseous mixture can be calculated using the following equation--think Daltons Law of Partial Pressures here.
Demonstrate an understanding of partial pressures and mole fractions. Daltons law also called Daltons law of partial pressures states that in a mixture of non-reacting gases the total pressure exerted is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases. Daltons law of partial pressure.
Daltons Law of Partial Pressures. P He P Ne P total. Partial Pressure Definition Partial pressure is a term used to describe the portion of pressure that one specific substance exerts when examining an entire gas.
P tells us that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the pressures that would be exerted by each gas if it alone occupied the total volume. Definition of partial pressure and using Daltons law of partial pressures If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website.

Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure Physical Chemistry Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure Use And Formulas
Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressures Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressures Estimation Applications Of Dalton S Law
Instrumentation And Measurement Of Atmospheric Pressure

Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressures Calculating Partial Total Pressures Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure Ppt Download
What Is The Application Of Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure Quora
Taher Technical Gyan Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressures States That The Total Pressure Of A Mixture Of Gases Is The Sum Of The Partial Pressures Of Its Components P Total

Temperature Problems Caused By Air Tlv A Steam Specialist Company Uk

0 Response to "Dalton's Law Of Partial Pressure"
Post a Comment