Allocative Inefficiency Definition
The audit opinion is intended to provide reasonable assurance but not absolute assurance that the financial statements are presented fairly in all material respects andor give a true and fair view in accordance with the financial reporting framework. X-inefficiency occurs when technical-efficiency is not achieved.
Allocative Efficiency
1
Lesson Overview Consumer And Producer Surplus Article Khan Academy
Allocative efficiency occurs when the firms price P.

Allocative inefficiency definition. Allocative inefficiency Allocative inefficiency means that the typesquantities of goods or services produced are not what is best for consumers. Allocative efficiency under perfect competition. Inefficiency in a Monopoly.
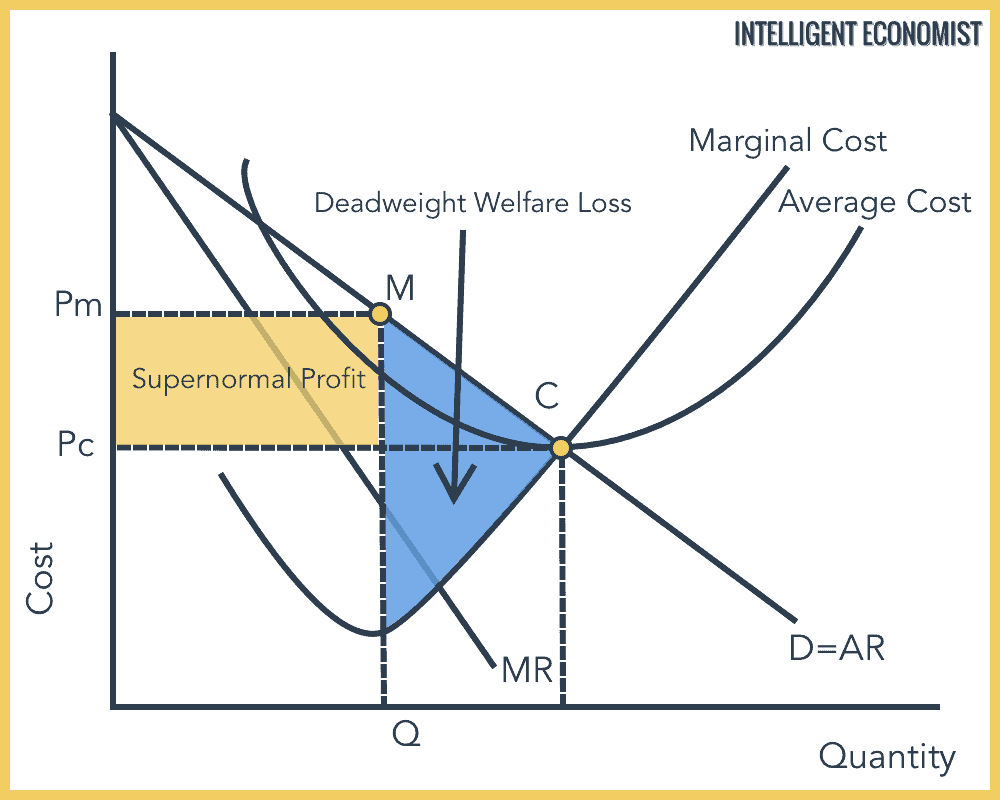
At profit maximisation MC MR and output is Q and price PGiven that price AR is above ATC at Q supernormal profits are possible area PABC. Inefficiency in the use of resources may translate into higher costs of goods and services and lower profits which may slow innovation. Section 2 of the report describes the concept and definition of efficiency and outlines the framework used for analysing efficiency in the context of a health system.
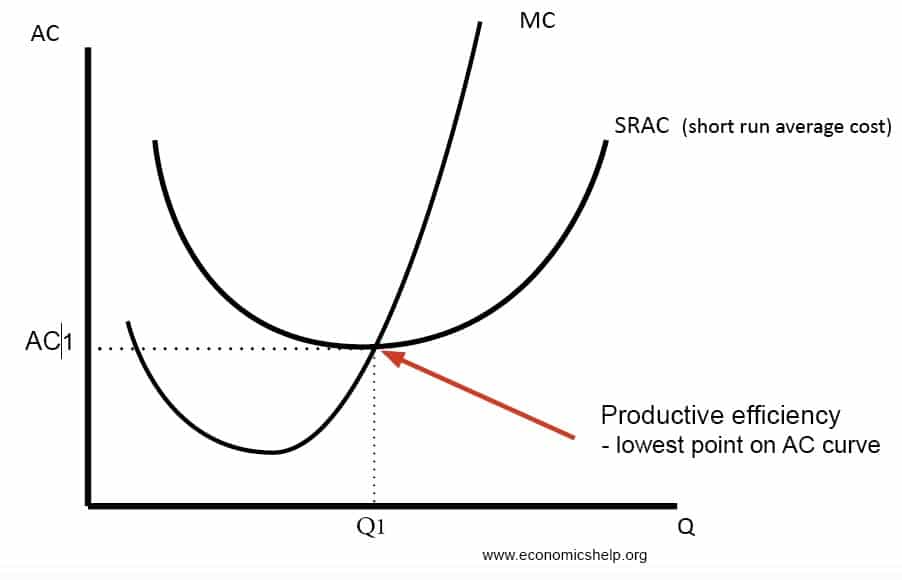
Allocative efficiency is quite different and is more concerned with the distribution and allocation of resources in society. 6 Such a societal perspective is rooted in welfare economics and has implications for the definition of opportunity costs. Productive inefficiencyTechnical inefficiency When resources are not used appropriately to produce the maximum number of goods at the lowest cost and best quality.
Furthermore corruption engenders allocative inefficiency by authorizing the least efficient contractor with the highest ability to bribe to be the recipient of government contracts. Most people criticize monopolies because they charge too high a price but what economists object to is that monopolies do not supply enough output to be allocatively efficient. X-efficiency measures how close to optimal efficiency a firm is operating in a given market.
The good use of time and energy in a way that does not waste any. The purpose of an audit is to provide an objective independent examination of the financial statements which increases the value. If the price of plywood was kept too low the result was allocative inefficiency a shortage.
In a monopoly the firm will set a specific price for a good that is available to all consumers. Allocative Efficiency definition. Section 4 is a synthesis of the lessons learnt.
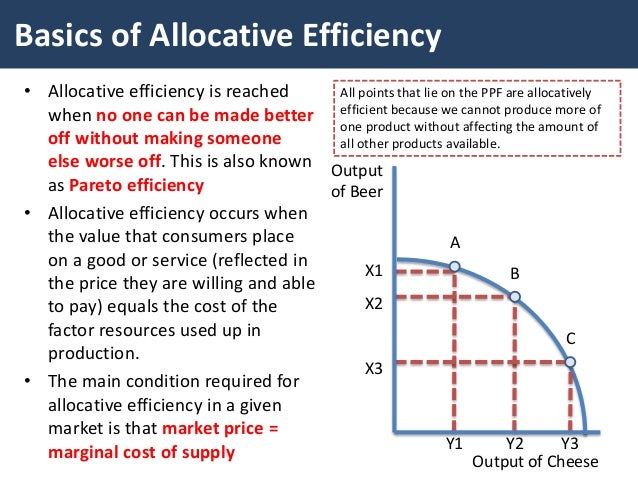
Allocative inefficiency occurs when the consumer does not pay a n efficient price. Monopolistic competitive markets have highly differentiated products. An allocation of resources such that no change in spending priorities could improve the welfare of one person without reducing the welfare of another.
True or false the competitive market system tends to drive the economy towards productive and allocative efficiency. Allocative efficiency looks at the marginal benefit of consumption compared to the marginal cost. X-Inefficiency X-efficiency and x-inefficiency are the same economic concept.
A Flour A I 1. The monopoly pricing creates a deadweight loss because the firm forgoes transactions with the consumers. In the 5Es lecture on Productive efficiency we defined it as producing at a minimum cost.
Section 3 summarizes the forms of inefficiency and the policy interventions described in each of the 10 country cases. Why is the monopolists outcome of producing and selling not allocatively efficient. A failed strategy project or product can dramatically reduce the efficiency of an organization by dedicating capital and spending to activities that create no value.
Firms can freely enter and exits in the long-run. The concept of allocative efficiency takes account not only of the productive efficiency with which healthcare resources are used to produce health outcomes but also the efficiency with which these outcomes are distributed among the community. Markets and Market Failure.
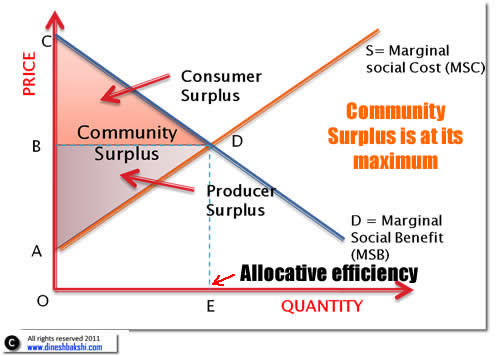
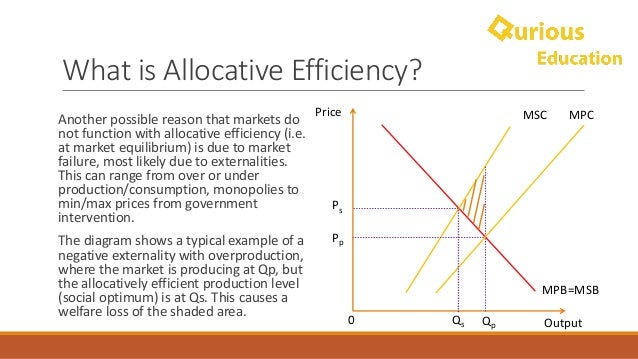
BORK supra note 23 at 72-89. A more precise definition of allocative efficiency is at an output level where the Price equals the Marginal Cost MC of production. A n efficient price is one that just covers the costs of production incurred in supplying the good or service.
The problem of inefficiency for monopolies often runs even deeper and involves inefficiency over a longer period of time. Allocative efficiency will occur at an output when marginal benefit price marginal cost. To understand why a monopoly is inefficient it is useful to compare.
The Inefficiency of Monopoly. Prices are also very important in maintaining productive efficiency. Equilibrium is a state in which market supply and demand balance each other and as a result prices become stable.
Many employers believe that monitoring is necessary to prevent loss of trade secrets abuses of their computer networks and inefficiency and loss of productivity through wasted time. The second source of inefficiency is the fact that these firms operate with excess capacity. Whenever an input is not used effectively the difference between the actual output and the maximum output attributable to that input is a measure of the degree of X-efficiency.
Attitude to Health Public attitudes toward health disease and the medical care system. The quantity of the good will be less and the price will be higher this is what makes the good a commodity. Output per hour of work is the definition of.
Introduced to the definition measurement of the macroeconomic variables like GDP consumption savings investment and balance of payments. Eventually all super-normal profits are e. Allocative Efficiency Allocative efficiency is the deployment of resources to create value.
The Inefficiency of Monopoly. Have many firms providing the good or service. Most people criticize monopolies because they charge too high a price but what economists object to is that monopolies do not supply enough output to be allocatively efficient.
There is some degree of market power. Allocative Efficiency Assesses competing programs and judges the extent to which they meet objectives. The difference between the.
To understand why a monopoly is inefficient it is useful to compare. And buyers and sellers have imperfect information. Firms can make decisions independently.
Monopolistic competition in the short run. As new firms enter the market demand for the existing firms products becomes more elastic and the demand curve shifts to the left driving down price. Definition of allocative efficiency This occurs when there is an optimal distribution of goods and services taking into account consumers preferences.
Those analysts believe that the only cognizable harm from market power is allocative inefficiency. In addition since the cost of bribes is included in the price of the goods produced demand tends to be reduced the structure of production becomes biased and consumption falls below efficiency levels. Others argue that the consumer welfare Congress intended to protect is a broader concept.
Productive Vs Allocative Efficiency Economics Help
Economic Efficiency In Markets And Industries
Allocative Efficiency Intelligent Economist
Allocative Efficiency A State Of The Economy Zoefact
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_INV_final_Allocational_Efficiency_Jan_2021-012-8e1bff8c4ccd4e36a7d14530238d4ed0.jpg)
Allocational Efficiency Definition

Sage Reference Encyclopedia Of Education Economics Finance
Allocative Efficiency
Market Efficiency Notes A Level Ib Economics
0 Response to "Allocative Inefficiency Definition"
Post a Comment