In Which Way Are Vesicles Different From Vacuoles
They form the cytoskeleton. Generally small in size 2.

By Yosuke Mathew And Jenny Ppt Video Online Download
What Is The Difference Between A Vesicle And A Vacuole Quora

Learning Target Eukaryotic Cell Organelles I Can Describe The Structure And Function Of Common Organelles In A Typical Eukaryotic Cell To Achieve This Ppt Download
Both types of cells have vacuoles storage units for food and liquid.
In which way are vesicles different from vacuoles. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes may be single-celled organisms. Lysosomes are specialized vesicles in which protein enzymes are contained. They are of different types of lysosomes peroxisomes.
Vacuoles can store different substances depending on the type of cell they are in. There are Different Types of Vesicles They are as Follows. Location of protein synthesis - Structure.
Vacuoles are smaller in size and less in number 5. Smaller vesicles containing the same substances as the vacuole which transported these substances to the central vacuole. Large molecules such as proteins polysaccharides and nucleotides and even whole cells are moved in and out of cells by using membrane vesicles.
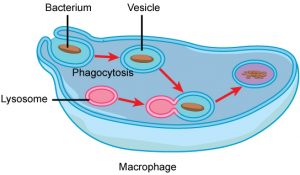
Amoebas paramecia and yeast are all single-cell eukaryotes. Phagocytosis or cell eating is the process by which a cell engulfs a particle and digests it. Animal cell vacuoles are typically small and each cell can contain multiple vacuoles.
Plastids are absent 4. This includes solutions that have been created and are being stored or excreted and those that have been phagocytized or engulfed by the cellA vacuole is simply a chamber surrounded by a membrane which keeps the cytosol from being exposed to the contents inside. Endosome and lysosome compartments are characterized by their morphological and functional properties.
Lysosomes function as the digestive system of the cell serving both to degrade material taken up from outside the cell and to digest obsolete components of the cell itself. Weber in Encyclopedia of Neuroscience 2009 Endosome to Lysosome with Stops along the Way. Vacuoles containing a variety of different materials are found outside of the cell and once absorbed through the cell membrane the lysosomes fuse with the vacuoles and begin digesting them.
The membrane holds fluid called cell sap which is composed of water and other substances. Both cells carry DNA and rDNA ribosomal DNA Both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells have vesicles. Vesicles back to top The processes described so far only apply to small molecules.
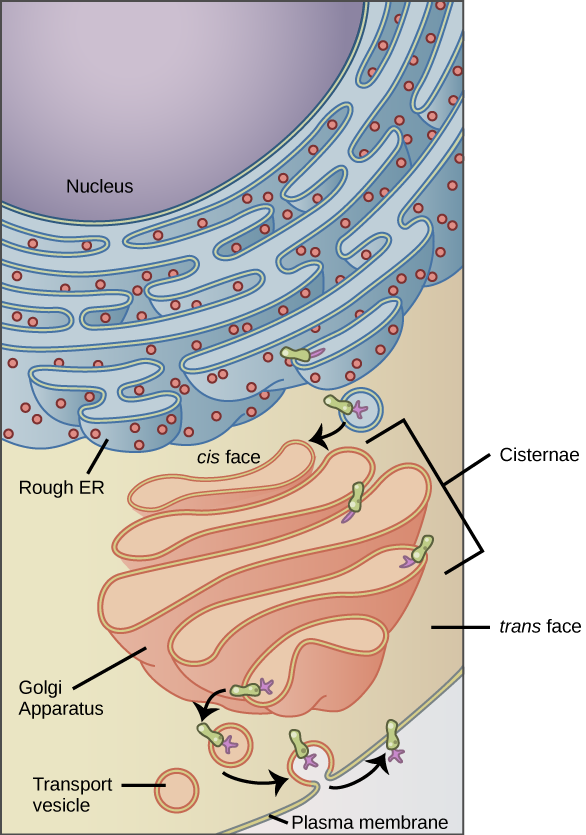
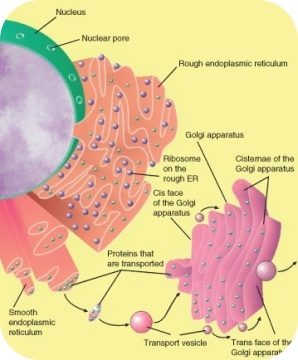
These are small-sized sac-like structures. The lysosomes break down macromolecules into their components for further use by the cell. Hormones neurotransmitters - are packaged in secretory vesicles at the Golgi apparatusThe secretory vesicles are then transported to the cell surface for release.
Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles that contain an array of enzymes capable of breaking down all types of biological polymersproteins nucleic acids carbohydrates and lipids. Produces lysosomes - Structure. Cell secretions - eg.
Plastids are present 4. Three primary mechanisms of endocytosis that are exhibited by a typical cell are illustrated in Figure 1. The contractile vacuole is a specialized type of vacuole that regulates the quantity of water inside a cellIn freshwater environments the concentration of solutes is hypotonic lesser outside than inside the cellUnder these conditions osmosis causes water to accumulate in the cell from the external environment.
The membranes of vesicles can fuse with either the plasma membrane or other membrane systems within the. In cell biology a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayerVesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion uptake endocytosis and transport of materials within the plasma membraneAlternatively they may be prepared artificially in which case they are called liposomes not to be confused with lysosomes. Other than the fact that vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles there is a very subtle distinction between them.
Creates vesicles to enclose materials to be secreted. Centrioles are absent Animal cell Plant cell 38. Cell wall is present 3.
The size of vesicles varies and those larger than 100 nanometers in diameter are typically referred to as vacuoles. Back then Quattrocchio and Koes led a team that discovered a completely new type of component of plant cells. Vacuoles serve many functions.
These data point to the Golgi-endosomal system as being a key route for the production of ATG9 vesicles that could nucleate the domain forming the omegasome directly fuse with the growing phagophore membrane or reside dynamically in a larger intermediate compartment called the ATG9 compartment Fig. Generally large in size 2. The word phagocytosis comes from the Greek phago- meaning devouring and -cyte meaning cellCells in the immune systems of organisms use phagocytosis to devour bodily intruders such as bacteria and they also engulf and get rid of cell debris.
Such plants that have vacuoles may not appear healthy and need a lot of water. They called these extra vacuoles vacuolinos Italian for small vacuoles. A vacuole is an organelle in cells which functions to hold various solutions or materials.
Which of the following would be a way of finishing this hypothesis about the function of the Golgi apparatus. Two subunits of RNA and protein synthesized in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Endosomes are typically involved with the sorting and delivery of lipid vesicles and their contents to and from the plasma membrane.
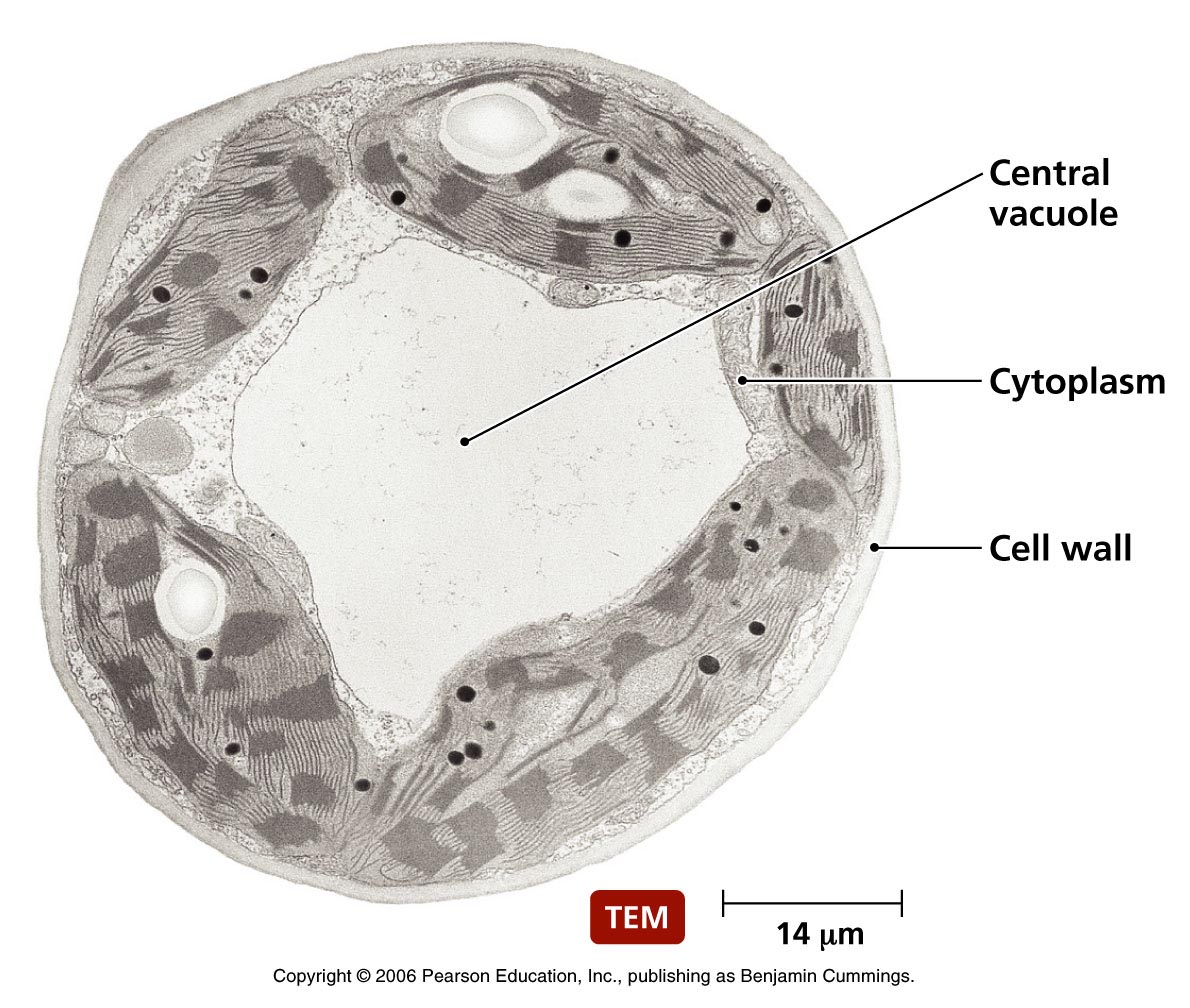
It is a sac surrounded by a single membrane called a tonoplast. Stacked flat single-membrane sacs - Plant or Animal. Vacuoles are a kind of storage bubbles present in the plant cells.
The way lysosomes perform their function is the subject of a great deal of current research. Vesicles are similar to vacuoles but are part of the transportation system of the cell. Vacuoles can even store food products or a variety of different nutrients that a cell would require to live.
Endocytosis is the transport of materials into a cell. Cell wall is absent 3. The vacuole is a type of organelle present in eukaryotic cells.
These are filamentous extensions in the cytoplasm. Every cell is enclosed in a membrane a double layer of phospholipids lipid bilayerThe exposed heads of the bilayer are hydrophilic water loving meaning that they are. However they do these things in different ways.
2 which appears as a collection of small vesicles tubules and vacuoles. Animal and plant 2. This includes the information on each vesicles parts and the way theyre assembled.
Vacuoles are pouches in the cell that store materials such as water salts proteins and carbohydrates. Centrioles are present 1. Results to date suggest that the days of viewing lysosomes as stand alone processing plants are numbered but perhaps we should take the view that there are probably different types of lysosomal systems and that no one model offers universal application.
Golgi apparatus is involved in repair and synthesis of cell membranes Lysosomes are formed by Golgi apparatus All types of substances which are to be secreted or excreted are packed in vesicles by Golgi apparatus for passage to the outside Takes part in storage modification and packaging of various biochemical produced by different components of the cell Components of cell wall are. Vesicle dysfunction is assumed to contribute to Alzheimers disease diabetes some hard-to-treat cases of epilepsy immunological disorders and certain neurovascular conditions. Vesicles and vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that function in storage and transport.
Vacuoles are larger in size and more in number 5. If the Golgi apparatus is involved in packaging products for secretion then A vesicles must travel from the Golgi to the cell surface. Specialized vesicles can also be involved in cellular metabolism.
The contractile vacuole acts as part of a protective mechanism that. Vacuoles outside the cell can contain a variety of different compounds. For example in fat cells vacuoles will often store large amounts of lipids.
Vacuoles in animal cells also help with the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis. For example white blood cells are types of phagocytes.
What Is The Difference Between A Vesicle And A Vacuole Quora
Vesicles And Vacuoles Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation
1
Vesicles Transport Information

Vesicles And Vacuoles Lysosomes And Peroxisomes Principles Of Biology

Difference Between Vacuoles And Vesicles Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Vesicles And Vacuoles Lysosomes And Peroxisomes Principles Of Biology

Difference Between Vacuoles And Vesicles Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
0 Response to "In Which Way Are Vesicles Different From Vacuoles"
Post a Comment