Muscarinic And Nicotinic Receptors
There are three types of muscarinic receptors. Activated Gα subunits then interact with an effector molecule to produce a second messenger which then brings about a cellular response Table 3.
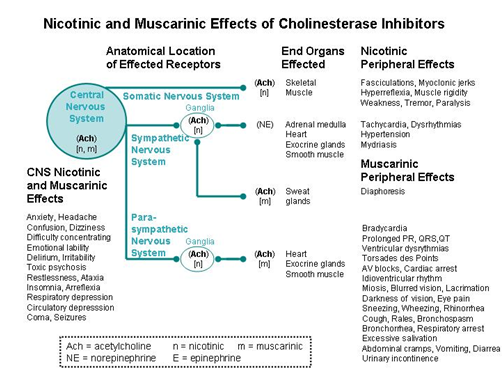
Cholinesterase Inhibitors Part 4 The Cholinergic Toxidrome Section 1 What Is The Cholinergic Toxidrome Environmental Medicine Atsdr

Cholinomimetics Direct Agonists Osmosis

Cholinergic Receptor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The pupillary constrictor muscle depends on muscarinic cholinoceptor.

Muscarinic and nicotinic receptors. EZmed defines beta adrenergic receptor type 1 2 and 3 function structure location and stimulation effects in the heart lungs kidneys eye and blood vessels by responding to catecholamine and neurotransmitters like epinephrine and norepinephrine to generate a sympathetic fight or flight resp. M1 receptors excitatory receptors present. They are stimulated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine released at the nerve endings.
Receptor pharmacology is the study of the interactions of receptors with endogenous ligands drugspharmaceuticals and other xenobiotics. ACh may bind either muscarinic or nicotinic receptors. Muscles in the gastrointestinal tract during anesthesia and to treat motion sickness.
The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor likewise gets its name from a chemical that selectively attaches to that receptor muscarine. These receptors are translocated to the nucleus after stimulation by an agonist. Nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors.
Its potency at nicotinic receptors is much lower and actions at non-muscarinic receptors are generally undetectable clinically. ACh is synthesized in cholinergic neurons such as those in the nucleus basalis of Meynert from choline and acetyl-CoA using an enzyme called choline acetyltransferase. Acetylcholine acts on two types of receptors.
This is usually secondary to the inactivation or inhibition of acetylcholinesterase AChE. All the muscarinic receptors are G-protein coupled receptor types. Type I intracellular receptors located in the cytoplasm of a cell.
As acetylcholine is the main neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic system these antagonists can successfully block the entire parasympathetic activation. Hence along with the nicotinic receptors they are called cholinergic receptors. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors mAChR These receptors are seven transmembrane G-protein coupled receptors.
Others selectively block M3 a specific type of muscarinic receptor. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors or mAChRs are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other cellsThey play several roles including acting as the main end-receptor stimulated by acetylcholine released from postganglionic fibers in the parasympathetic nervous system. Which means that when ACh binds to it ions flow through it.
Cholinergic receptors function in signal transduction of the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. Atropine is relatively selective for muscarinic receptors. In order to understand the molecular mechanism underlying a ligands effect on physiological or therapeutic cellular responses a number of basic principles of receptor theory must be considered.
Muscarinic receptors comprise one of the two classes of receptors for the neurotransmitter acetylcholine with nicotinic receptors comprising the other class. The same neurotransmitter binds to them yet their mechanism of action MOA differs quite greatly due to their uniqueness. Heres what Ive got.
Type II intracellular receptors located in the nucleus of a cell even in the absence of agonists. Some urinary antispasmodics are non-selective which means they bind to both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. For example nicotinic receptors are located in the blood vessels and can modulate blood flow.
Finally the ganglion type nicotinic receptor is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor that is located in the autonomic ganglia. They are not as common as muscarinic receptors in the central nervous system. It acts as a channel for positively charged ions mainly sodium.
Nicotinic and muscarinic receptors are the two main types of cholinergic receptors. Atropine and scopolamine inactivate muscarinic receptors and are used to suppress bodily secretions eg. From a systems perspective nicotinic receptors have a role in directly stimulating not only pre- and postsynaptic neurons but also other functions.
Tears or mucus and to relax smooth muscle eg. They are integral membrane proteins activated by the binding of acetylcholine a neurotransmitterThough the same neurotransmitter binds to both types of receptors the mechanism of action is different in each receptor. Abbreviated as ChAT this is an enzyme that is synthesized within the body of a neuron.
Activation of a GPCR allows interaction with a G-protein which is composed of α β and γ subunits. Nicotinic receptors get their name from nicotine which does not stimulate the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors but selectively binds to the nicotinic receptors instead. O Examples androgen AR glucocorticoid GRa mineralocorticoid MR and progesterone receptors PR.
Cholinergic crisis is a clinical condition that develops as a result of overstimulation of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors at the neuromuscular junctions and synapses. Muscarinic receptors are a part of the parasympathetic system. These include adrenergic muscarinic and opioid receptors.
Hexamethonium and trimethaphan block nicotinic receptors and are used to reduce high blood pressure. Nicotinic and Muscarinic receptors are both Acetylcholine ACh receptors. These receptors subdivide into nicotinic and muscarinic receptors which are named secondary to separate activating ligands that contributed to their study.
The structure of the receptors varies between tissues and different times in development. First off Nicotinic Receptors are ionotropic. Muscarinic receptors are selectively activated by the alkaloid muscarine from the mushroom Amanita muscaria and are blocked by belladonna alkaloids such as atropine and scopolamine Figure 1.
Atropine does not distinguish among the M1 M2 and M3 subgroups of muscarinic receptors. Main Difference Nicotinic vs Muscarinic Receptors. The receptors are named because they become activated by the ligand acetylcholine.
The muscarinic receptor antagonists bind to acetylcholine receptors and prevent their activation. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are ligand-gated ion channels and muscarinic receptors are G protein-coupled. They show their response in few seconds to minutes unlike nicotinic receptors which show.
Although nicotinic receptors are also present throughout the lungs and are crucial for neurotransmission between pre- and postganglionic parasympathetic nerves muscarinic receptors are a major physiological target for acetylcholine in the lungs and are the primary focus of this chapter.

Pharmacology Of Muscarinic Receptor Blockade Acetylcholine Is An Agonist At Both Muscarinic And Nicotinic Receptors The Nicotinic Actions Of Acetylcholine Ppt Download

Nicotinic Vs Muscarinic Receptors Youtube
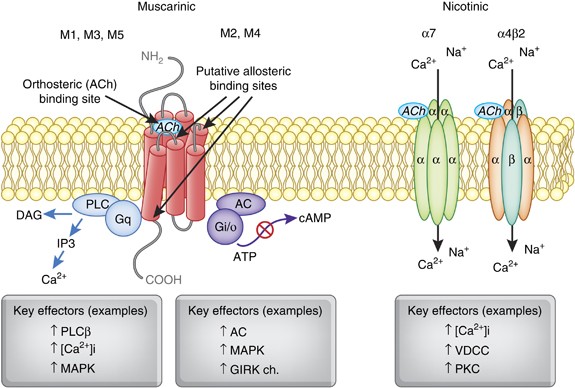
Muscarinic And Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonists And Allosteric Modulators For The Treatment Of Schizophrenia Neuropsychopharmacology
Cholinergic Drugs I Nicotinic And Muscarinic Receptors Chemistry Libretexts

Figure 6 Role Of M2 Muscarinic Receptor In The Airway Response To Methacholine Of Mice Selected For Minimal Or Maximal Acute Inflammatory Response

Acetylcholine Receptor Wikipedia
3

Plasticity Between Nicotinic And Muscarinic Acetylcholine Ach Download Scientific Diagram
0 Response to "Muscarinic And Nicotinic Receptors"
Post a Comment